C bit And Big Little Endian
The tencent engineer asked a question about the C bit, I could not answer it with a pretty description. so there is a summary for it.
Bit Little Endule
for exmaple: 32bit int(uint32_t) data : 0x12345678,store in address : 0x08004000:
| Address |
Little Endian |
Big Endian |
| 0x08004003 |
0x12 |
0x78 |
| 0x08004002 |
0x34 |
0x56 |
| 0x08004001 |
0x56 |
0x34 |
| 0x08004000 |
0x78 |
0x12 |
CPU
little-endian
X86
ARM(default)
big-endian
PowerPC
IBM
Host to network bit
htonl()
htons()
Network to host bit
ntohl()
ntohs()
Check Big & Little Endian
Int char check
1
2
3
4
5
6
| int i = 1;
char *p = (char *)&i;
if(*p == 1)
printf("Little Endian");
else
printf("Big Endian");
|
union check
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| int checkCPUendian()
{
union
{
unsigned int a;
unsigned char b;
}c;
c.a = 1;
return (c.b == 1);
}
|
Parse bit field
We need to parse the data protocal, and there are many key-value in bit mode, usually we will use the right shift to get the target bit.
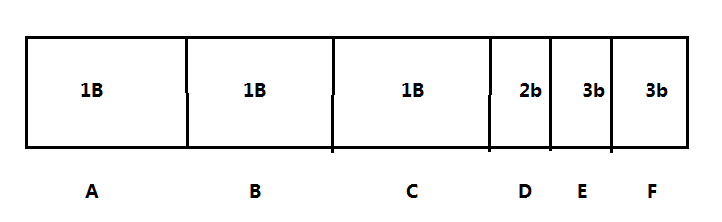
D will be : ((pucPktAddr + 3)>>6) & 0x3 –point shift 3 bytes, and right shift 6 bit,then apply mask 0x3
E will be : ((pucPktAddr + 3)>>3) & 0x7
Now we try bit mode
Bit mode
1
2
3
4
5
| 1 typedef struct XXX {
2 unsigned char D:2
3 unsigned char E:3
4 unsigned char F:3
5 }
|
then we can use xxx->D,xxx->E,xxx->F to access the data,but this is only in big end mode, if you want to use light end mode,try to reverse it:
1
2
3
4
5
| 1 typedef struct XXX {
2 unsigned char F:3
3 unsigned char E:3
4 unsigned char D:2
5 }
|
大小端序数据相互转换函数
将unsigned char数组转换成“大端序”整数;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
int MULCONVERSE_CALL ConverseArrayToBeUI(unsigned char *srcArray,unsigned int *desBeData)
{
if (srcArray == NULL_POINT || desBeData == NULL_POINT)
{
return ERR_NULL_POINT;
}
*desBeData = (unsigned int)(srcArray[0]<<24) + (unsigned int)(srcArray[1]<<16) +
(unsigned int)(srcArray[2]<<8) + (unsigned int)srcArray[3];
return _SUCCESS;
}
|
将unsigned char数组转换成“小端序”整数;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
int MULCONVERSE_CALL ConverseArrayToLeUI(unsigned char *srcArray,unsigned int *desLeData)
{
if (srcArray == NULL_POINT || desLeData == NULL_POINT)
{
return ERR_NULL_POINT;
}
*desLeData = (unsigned int)(srcArray[3]<<24) + (unsigned int)(srcArray[2]<<16) +
(unsigned int)(srcArray[1]<<8) + (unsigned int)srcArray[0];
return _SUCCESS;
}
|
将整数按照“大端序”格式存储在数组中;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
int MULCONVERSE_CALL ConverseUItoBeArray(unsigned int srcData,unsigned char *desBeArray)
{
if (desBeArray == NULL_POINT)
{
return ERR_NULL_POINT;
}
desBeArray[0] = (unsigned char)(srcData>>24);
desBeArray[1] = (unsigned char)(srcData>>16);
desBeArray[2] = (unsigned char)(srcData>>8);
desBeArray[3] = (unsigned char)srcData;
return _SUCCESS;
}
|
将整数按照“小端序”格式存储在数组中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
int MULCONVERSE_CALL ConverseUItoLeArray(unsigned int srcData,unsigned char *desLeArray)
{
if (desLeArray == NULL_POINT)
{
return ERR_NULL_POINT;
}
desLeArray[3] = (unsigned char)(srcData>>24);
desLeArray[2] = (unsigned char)(srcData>>16);
desLeArray[1] = (unsigned char)(srcData>>8);
desLeArray[0] = (unsigned char)srcData;
return _SUCCESS;
}
|
Big-Endian to Little-Endian
1
2
3
| #define BigtoLittle16(A) ((((uint16)(A) & 0xff00) >> 8) | (((uint16)(A) & 0x00ff) << 8))
#define BigtoLittle32(A) ((((uint32)(A) & 0xff000000) >> 24) | (((uint32)(A) & 0x00ff0000) >> 8) | \
(((uint32)(A) & 0x0000ff00) << 8) | (((uint32)(A) & 0x000000ff) << 24))
|
关于程序与设计 | kernel & MCU & ASIC Lover,Software Engineer | 这里是 @蛋种 的个人博客,与你一起发现更大的世界。

